Actively involving individuals and communities in the decision-making processes that affect their lives is the essence of citizen participation in government. Giving people a voice in shaping the futures of their communities achieves the true promise of democratic institutions and improves quality of life. The purpose of this guide is to explore best practices for driving citizen engagement by leveraging technology.
Understanding Citizen Participation in Government
Public meetings are typically where residents have an opportunity to participate in major projects that impact their communities. Unfortunately, public meetings are usually held at time and places that are not convenient for the majority of residents. As a result, citizen involvement suffers even though engagement processes are often required by law.
Innovative approaches like online platforms can help bridge the gap between governments and the communities they serve. By leveraging technology, a broader cross-section of the population can be reached regardless of demographic and socioeconomic factors. Technology is the key to involving a more diverse audience including working families and people of color in citizen participation.
Bridge the Gap Between Citizens and Government: Leverage Instant Input to Boost Participation and Collaboration. Try our citizen participation platform.
Try Instant Input TodayThere are four key objectives of citizen participation. These include:
- Fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment: When citizens are given the opportunity to participate in the decision-making processes that affect their communities, they have a stronger sense of ownership and freedom. Playing a supportive role helps with the development of a more active and informed citizenry. An engaged citizen is a “good citizen,” one who is truly invested in the future of their community.
- Increasing transparency and accountability: Public decision making can help ensure that decision-making processes are transparent and accountable. When citizens are engaged in civil society by providing input on decisions, they help hold public officials, civil servants and institutions accountable for their actions. Transparency and anccountability are critical components of deliberative democracy.
- Improving the quality of decisions: Involving a diverse group of citizens in decision-making is core to our political system and allows public authorities to draw on a wide range of perspectives, knowledge, and expertise. This approach takes into account the needs and interests of all stakeholders, resulting in better outcomes for the community.
- Enhancing collaboration and trust: Citizen participation builds trust and collaboration between citizens and public institutions. By involving citizens in the decision-making process, public authorities can show that they value and respect the perspectives of the community, and can work collaboratively with citizens to find solutions to complex problems. This instills a greater sense of freedom in our democracy.

How to Build a Citizen Participation System
A citizen participation system is a framework that allows members of society to have participation in the decision-making processes of government. With a tool like Instant Input, that can include informing and engaging the public about major road construction projects, infrastructure projects like water treatment plants, or community enhancements like parks and playgrounds, for example. Such participation platforms give residents a democratic voice in shaping decisions that affect their lives and instill a deeper sense of open government.
Systems should be designed with five key principles in mind. These are:
- Accessible information: Citizen participation systems seek to remove information asymmetries and communication barriers between governments and their communities. This is achieved in part by providing clear and easily understandable information about project goals, timelines, budgets, and project phase updates. The use of notifications can allow citizen participation systems to proactively push important project updates to members of the community, driving ongoing engagement.Citizen participation platforms should be designed for easy accessibility and use by people with disabilities. This includes people with visual, hearing and motor impairments among others.
- Inclusive engagement: Traditionally, government entities have gathered citizen feedback and shared project updates offline, through town meetings and civic forums that inherently have limited reach to a narrow segment of the population. Perhaps a few dozen people attend the typical town meeting. Older white retirees are overrepresented and have more power while other groups may be totally unrepresented. Working families, business owners, people with travel constraints, and many others who should have a seat at the table don’t get one because they simply can’t attend meetings.
- Two-way communication: Bi-directional communication between communities and their governments is essential to democratic institutions. When meetings are posted online, community members might receive useful information but not have an active channel to provide feedback or ask questions.Active participation platforms take offline project communication, updates and feedback processes online, allowing collaboration that spans demographic and socioeconomic groups. Two-way communication channels such as commenting and project surveys are among the most important features offered to project owners and citizens through platforms like Instant Input.
- Transparency: Citizens want to feel confident that their civil servants are committed to transparency. Citizen participation systems are designed to make public decisions as transparent as possible in the spirit of open government. Not only are citizens provided regular project updates and asked to engage with project feedback, they are also informed about how their input has influenced important decisions. They may be allowed to see how others have responded to engagement features like surveys, further building a sense of democratic society.
- Accountability: The transparency provided by citizen engagement systems increases stakeholder confidence in accountability. Platforms may include project documents pertaining to vendor bidding and awards, spend versus budget, vendor lists, and other information that builds trust through transparency and accountability.

Try Instant Input to See how We’re Helping Build Stronger Democratic Institutions and Communities. Revolutionize Your City’s Democracy: Use Instant Input to Strengthen Citizen Involvement and Trust.
Try Instant Input NowHere are some examples of projects that have leveraged technology to increase participation at the local level:
Participatory Budgeting (New York City): The Participatory Budgeting project allows residents to decide how to spend public money in their neighborhoods. Through a series of public meetings and events, members of the society can propose and vote on funding projects with the city budget.
Vision Zero (San Francisco): Vision Zero is a city-led effort to eliminate all traffic fatalities in San Francisco by 2024. The initiative includes public education campaigns, infrastructure improvements and policy changes. Community members are engaged to participate in the process of identifying high-risk areas and proposing solutions.
Housing Levy (Seattle): The Seattle Housing Levy is a property tax that funds affordable housing initiative in the city. The levy is subject to voter approval, and the city engages residents in the process of developing and refining proposals for how the money should be spent.
Open Budget (Chicago): The Open Budget project is a platform that provides citizens with accessible information about how the city spends its money. It includes public meetings and feedback mechanisms to ensure that citizens have a say in budget development and prioritization.
Hub2 (Boston): Hub2 was a pilot project that used the video game platform, Second Life, to engage citizens of Boston in planning a public park. A highly innovative citizen participation approach, Hub2 enabled community members to explore the proposed space from various visual perspectives. It also included feedback features and characteristics of citizen forums.
Middle Main Street Streetscape Improvement Project (City of Buffalo): Highland Planning collaborated with DiDonato Associates and Landscape Architect Joy Kuebler to co-host a series of pop-up events aimed at public deliberation on the proposed design for the reconstruction of Buffalo’s Main Street between Goodell Street and Ferry Street. This was done in support of the City’s Streetscape Improvement Project.
How to Promote Citizen Engagement
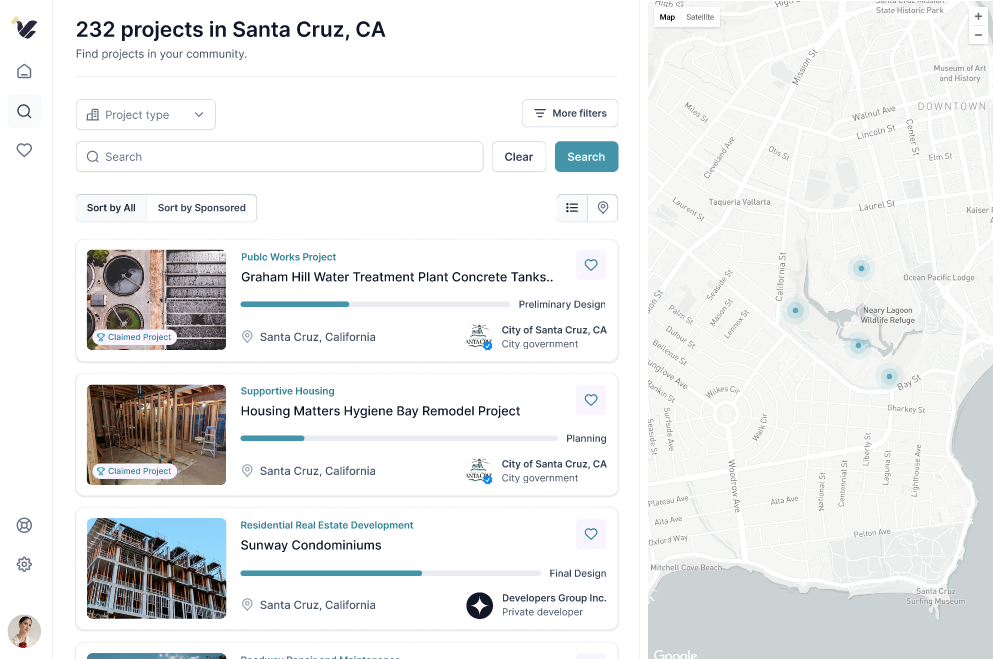
In the modern world, many different priorities compete for our attention on a minute-by-minute basis. The old idea of “build it and they will come” is simply no longer true. Reaching a broad audience is a major challenge for government project owners even when they provide project information online, for example through a .gov website. Some community members have told us that they don’t even bother looking for project information online because it’s just too piecemeal.
Instant Input seeks to solve this problem by featuring a wide range of searchable projects on a single platform. This allows the standardization of how information is presented and dramatically improves searchability versus projects that are featured on .gov websites.
Citizen Engagement Marketing Overview
Participatory processes typically begin with stakeholder interviews and stakeholder mapping to determine which members of the society are impacted by the project and who might be interested. For example, public transport may impact employers and workers, whereas park renovations may impact nearby families.
The benefit of Instant Input is that our community of users can self-select the locations and types of projects they want to review. This takes the guess work out of identifying stakeholders. Once stakeholders have been identified, engagement tactics can be developed to promote citizen participation.
If citizens are unaware of a project, it’s impossible for them to participate in the decision-making process. Thus, it is essential for project owners to overcome this obstacle through the use of marketing strategies and tactics. To that end, citizen participation platform providers should operate as strategic marketing partners for government project owners. Instant Input, for example, provides full funnel marketing and support services to build project awareness, engagement and trust with the community.
Offline Citizen Engagement Marketing
This type of marketing can include activities such as town hall meetings, community events, door-to-door canvassing, pop up events and direct mail campaigns. The goal is to reach people where they live, work and socialize, and to create opportunities for dialogue and feedback.
Offline approaches to gain citizen involvement may include tools like QR codes that can be posted at physical project sites. When scanned by a community member, the QR code should open a page containing all of the relevant project information, project documents and timelines, surveys, contact information and other features designed to build collaboration.
The limitation of onsite tools like QR codes is that they require a physical project location and may only reach pedestrian passersby. Since the goal of government project owners is to engage diverse community members from the pre-planning stages of projects, QR codes and other offline tactics are useful but incomplete solutions.
Online Citizen Engagement Marketing
Online engagement marketing approaches leverage the reach and speed of digital platforms to disseminate information quickly and efficiently. Online citizen engagement marketing can also help to reach audiences who may be more likely to engage in online activities and who may not have access to offline events. This is critical to achieving diversity, equity and inclusion goals.
Online citizen engagement marketing can include activities such as social media campaigns, email newsletters, online surveys, push notifications and virtual town halls. The goal is to create a digital space for dialogue and feedback that is accessible to the widest possible range of citizens.
In order to achieve citizen engagement at all project phases from pre-approval to completion, governments should share their projects on a citizen participation platform. However, one of the traditional weaknesses of platforms is that they’re usually just pop-ups sold to governments with little marketing support and zero built-in audience.
Aggregating projects into a single platform provides built-in community and stronger searchability. Adding content-marketing and social media support truly democratizes citizen involvement by proactively engaging people of all ages, backgrounds and circumstances where they are most often — online.
Instant Input is unique in that it hosts a wide range of projects from different project owners, not just a single source. This can increase project reach through content- and marketing-supported traffic concentrated into a single, independent platform that serves the needs of many.
How to Measure Citizen Engagement
Measuring citizen engagement can be challenging. Carefully defining a framework for measurement then implementing the systems and processes to track and report engagement is a complex task. Citizen participation platforms are designed to provide a turnkey solution for government project owners to measure engagement.
At a high-level, citizen participation metrics should include:
- Project Views: Who has seen your project and where are they located?
- Project Engagement: Who has commented, responded to your survey, etc.?
- Frequency and Duration of Participation: How deeply did your community engage and did they stay engaged?
- Demographic Data: Are you reaching a representative cross-section of your entire community?
Measuring citizen engagement is critical to understanding how well deliberative processes are working within a community. Measurement allows governments to understand who is being engaged effectively and who isn’t. This facilitates more inclusive practices and helps identify areas for improvement. It increases the effectiveness and legitimacy of project owner decisions.

The Future of Citizen Participation
The future of citizen participation will be informed by a commitment to equity, inclusion and collaboration. Achieving diverse participation will require augmenting traditional approaches with innovative technologies. Communities exist both as offline and online groups and citizen participation systems must seek to integrate these two worlds.
Artificial intelligence is an emerging area that will certainly impact and enhance citizen engagement. In addition to improving the scope and quality of information available for projects online, it will allow project owners and platform providers to better anticipate and analyze stakeholder feedback. Bi-directional communication and technical assistance with engagement processes will also be impacted through the use of chat bots to handle certain inquiries. While the implications of AI on citizen engagement will be profound, it is still too early to anticipate all the other forms these fundamental developments may take.
Conclusion
In summary, the goal of government project owners is to engage a fully representative group of their citizens rather than the narrow segment that attends traditional meetings. Open government platforms like Instant Input answer this challenge by increasing accessibility and inclusion. This helps build stronger communities and is a huge win for citizens, career civil servants and elected officials, regardless of their political parties, and across all socioeconomic groups.
Promoting citizen participation can be time-consuming as it requires specialized resources, ongoing management and an investment in bi-directional participation between project owners and stakeholders. For these reasons, many government entities elect to leverage the expertise and tools of private organizations and platforms like Instant Input.
Embrace the Future of Citizen Participation: Enhance Your City’s Engagement with Instant Input.
Try Instant Input TodayFrequently Asked Questions
What is the principle of citizen participation?The principle of citizen participation holds that that citizens have both a right and a responsibility to participate with their governments in the decision-making processes that affect them. This principle is based on the belief that decisions made by government should reflect the needs and interests of the people they serve. Citizen participation can take many forms, from attending public meetings to using online platforms.
Why is public participation important?Public participation is important because it allows people to have a voice in decisions that affect their lives, and it can help ensure that government and public officials are accountable to the public. When citizens are engaged in the decision-making process, they can help to identify challenges and solutions that might not otherwise be considered. Moreover, when citizens participate with project owners, they can work together to find solutions that are in the best interests of everyone involved.
What is an example of active citizen participation?There are many great examples of participatory governance where citizens have been given the opportunity to influence decisions in major municipal projects. These range from traditional offline approaches like town meetings to more innovative participation models. Modern participatory mechanisms include online platforms and hybrid online/offline models that help citizens participate with less effort. Technology-based methods include online surveys, interactive maps, social media campaigns, Web platforms and mobile apps, among others.
There are many more examples of governments leveraging traditional and technology-based methods to generate citizen interest and engagement in major projects. Using a combination of offline and online methods makes it easiest for residents to provide feedback, share ideas and participate in our political system.
What are the main objectives of citizen participation?The key objectives of citizen participation are to create more inclusive and effective decision-making processes by accounting for and incorporating the diverse needs and perspectives of a representative cross-section of the entire community?
How do you promote citizen participation with governments?One of the most important ways to promote citizen participation is to provide clear and accessible project information. Public authorities can create opportunities for citizens to participate through surveys, focus groups, public hearings, online forums and online citizen participation platforms. Social media campaigns, media coverage gained through public relations activities, online and offline events, and out of home advertising are all good options to help get the word out.